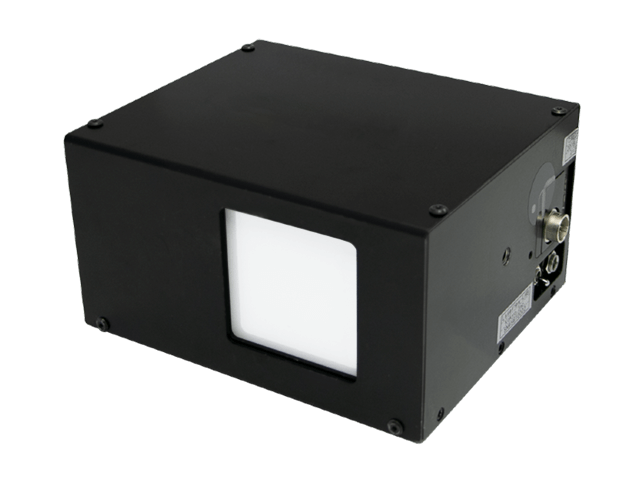
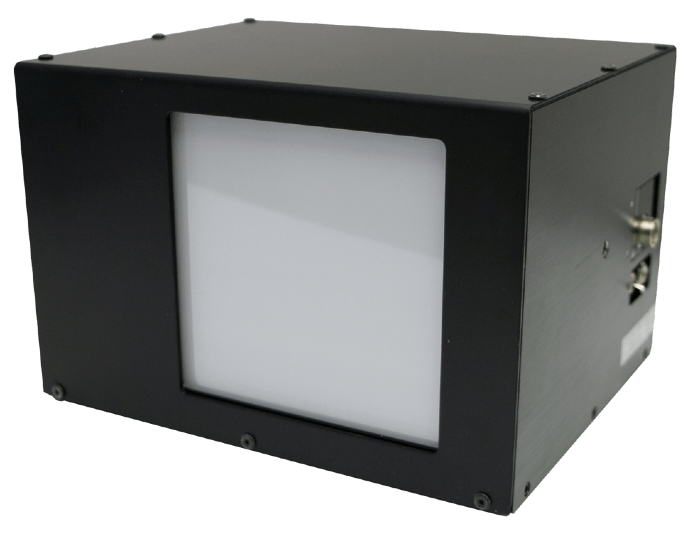
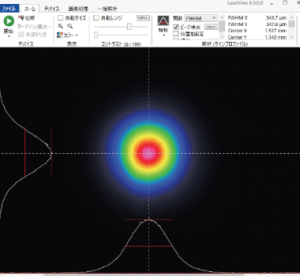
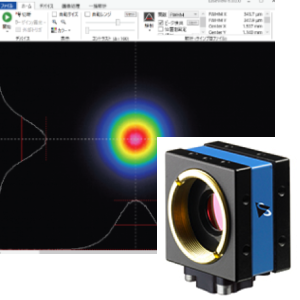
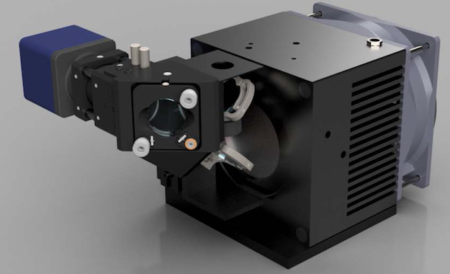
What is LBP-B ?
It works with the LaseView software, which is known for its great usability.
Equipped with different analysis capabilities, it is a very easy-to-use Laser Beam Profiler.
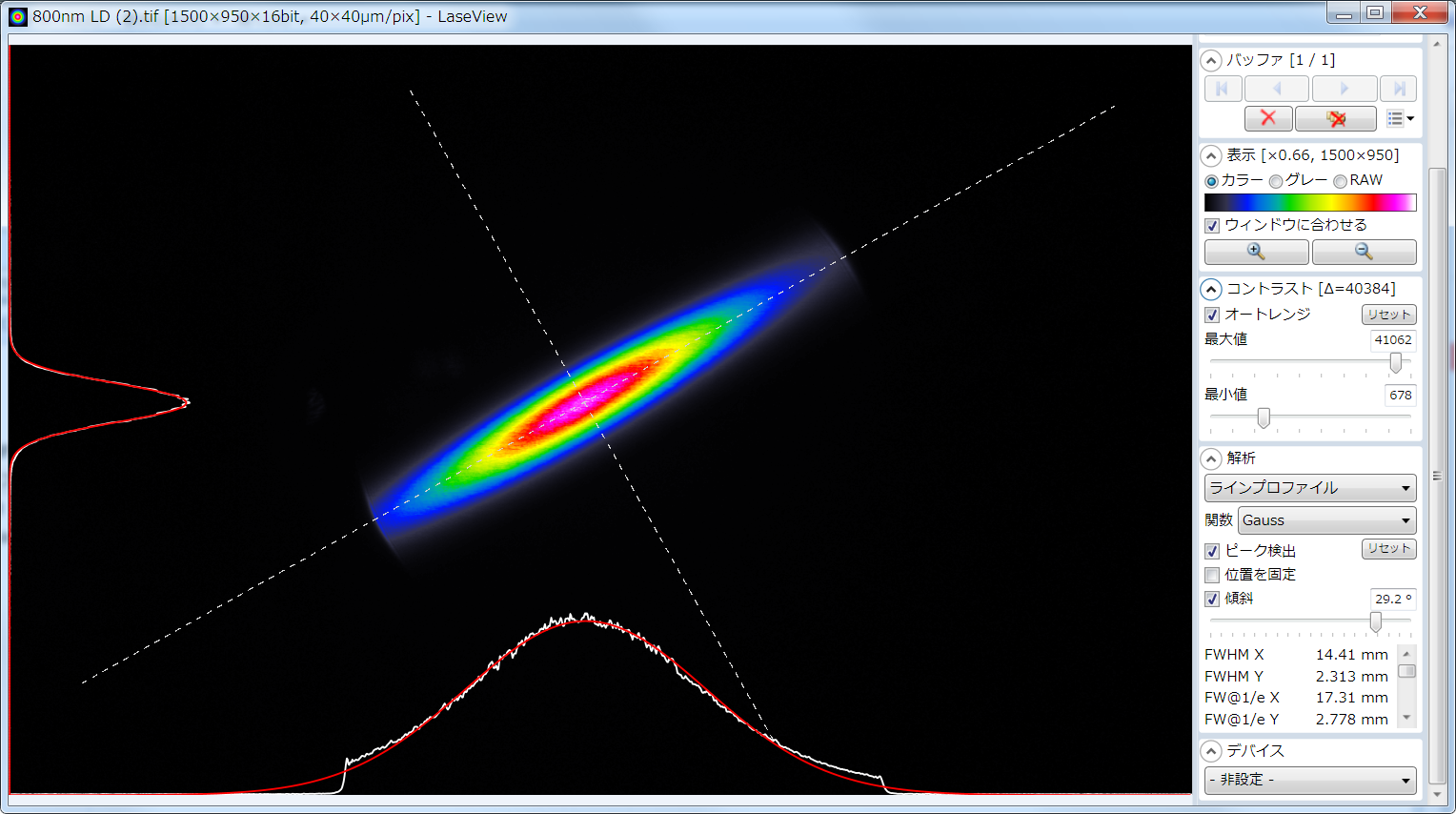
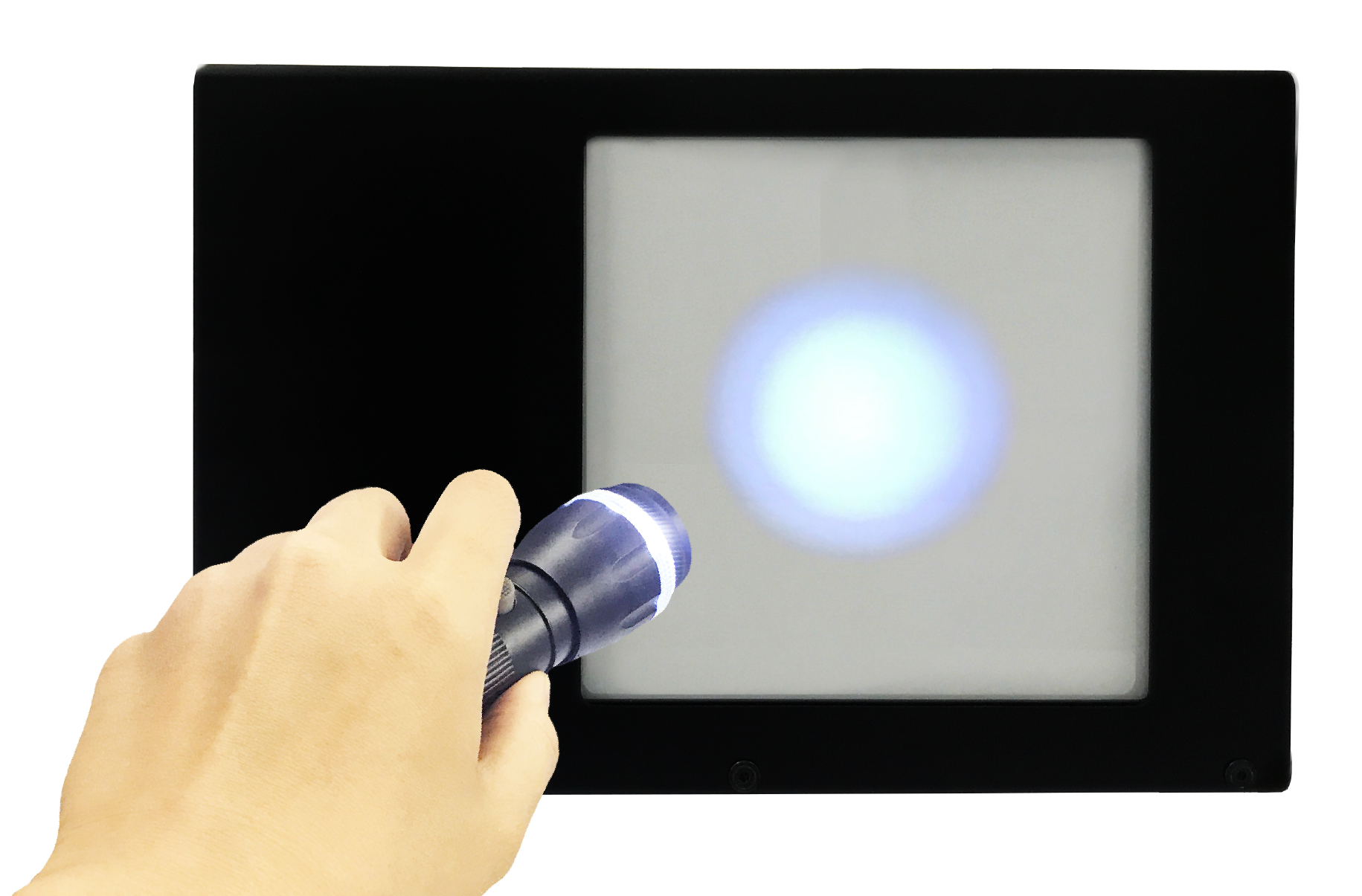
Fig: 808nm single-mode semiconductor laser’s diverging light
(FWHM: 14.4mmx2.3mm)
Features
- Measures easily the beam profile and diameter
- Can measure from small to large diameters (1mm – 200mm)
- Can measure high powers (0.1W/cm2 – 100 W/cm2)
- Includes speckle reduction function (patterns of bright and dark spots)
LaseView software Features
- Measures M2 beam quality
- Measures the beam Divergence Angle
- Evaluation of the beam power, beam profile between 2 points, and beam diameter changes available
- Measures the beam Pointing Stability over time

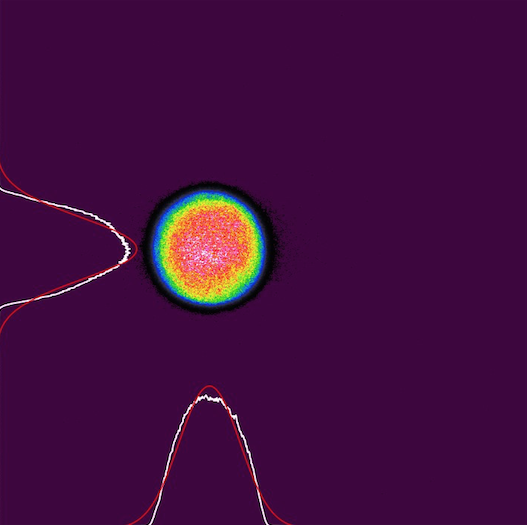
Measuring a beam with a diameter of about 15 mm and the software screen
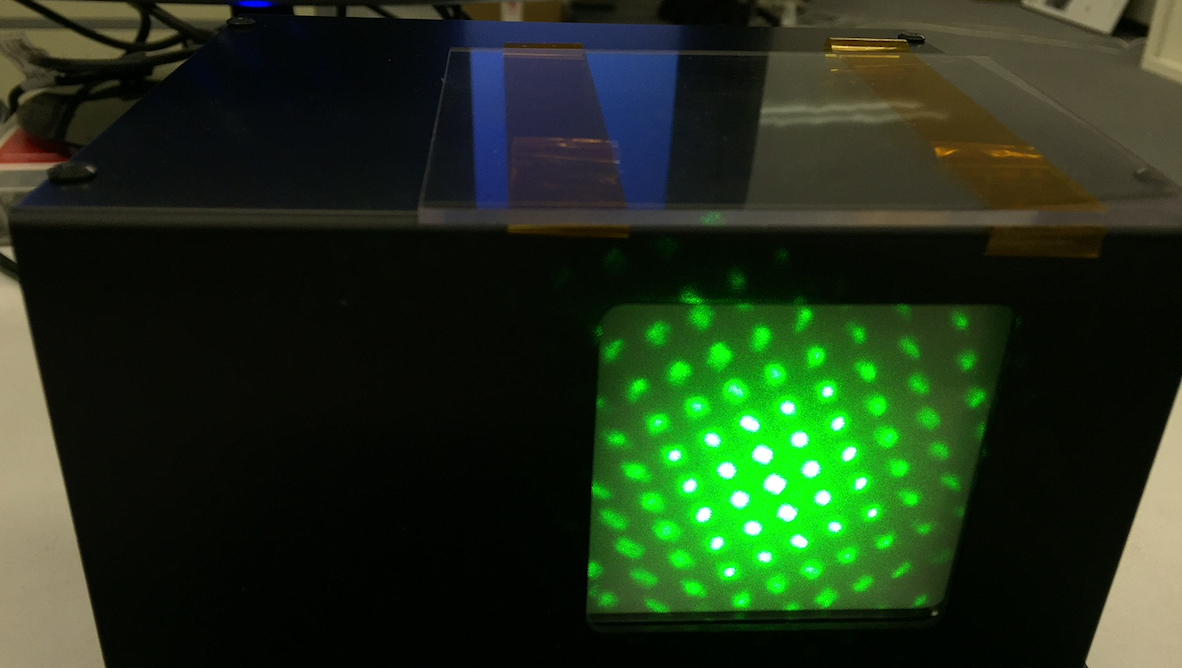
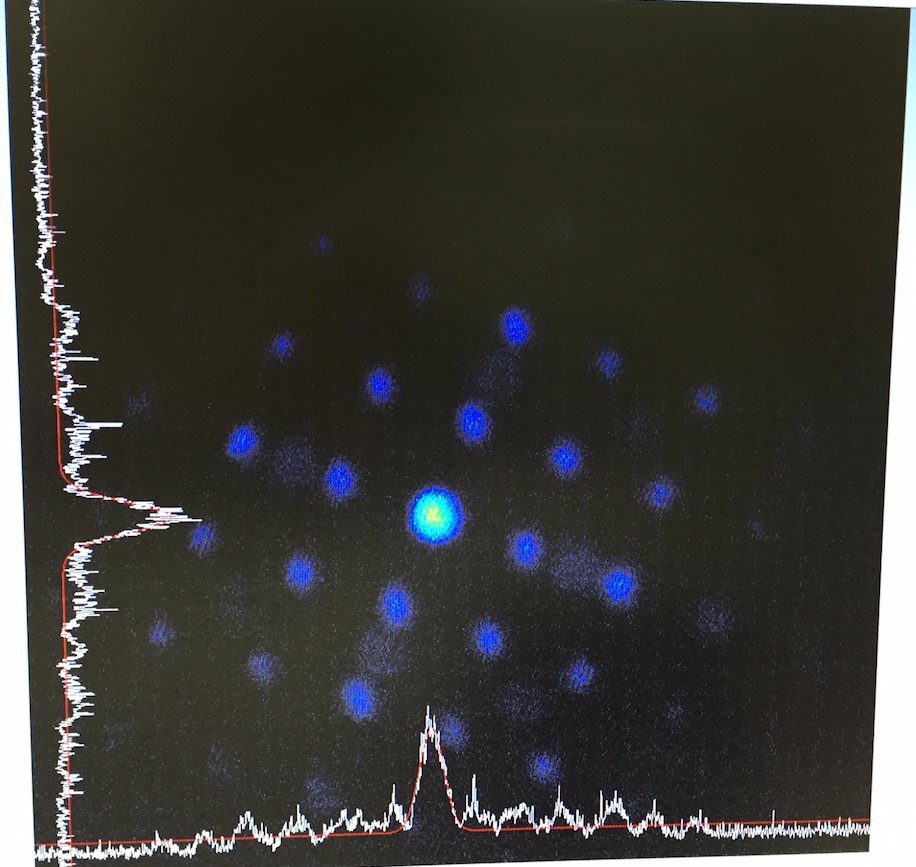
Measuring multi-point beam and software screen
LBP-B series lineup
Comparison between LBP-B and conventional products
For high power

Left : Laser Beam Profiling with dumped system.
Right: Laser Beam Profiling with at one time with LBP-B.
Fig: (by ASUKA MEDICAL Inc)
LBP-B can measure as much as maximum 100 W/cm2 laser beam without additional attenuation system by using a newly designed optical system.
It simplifies optical system and prevents introducing distortion on laser beam.
For large diameter

Left : Laser Beam Profiling by divided measurement.
Right: Laser Beam Profiling at one time by LBP-B.
Fig: (by ASUKA MEDICAL Inc)
Scanning laser measurement
Divergence angle Analysis function
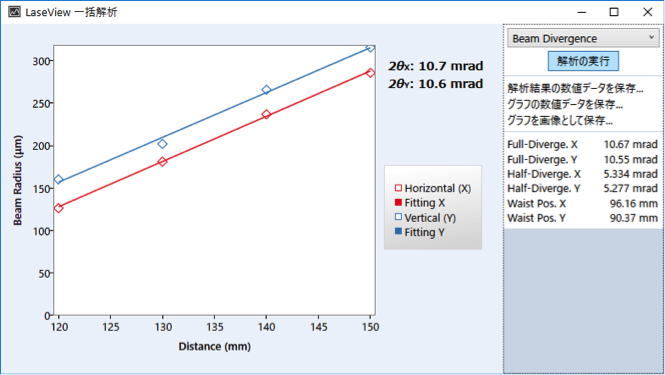
Fig: Beam divergence angle measurement screen
- Measurements taken at 2 or more positions shall be saved in the same folder.
- Click the “Divergence angle” button of “Collective analysis” tab.
In addition, as the measurements are made at different places, it is possible to evaluate the change in power and thus the propagation loss.
Beam pointing variation Analysis function
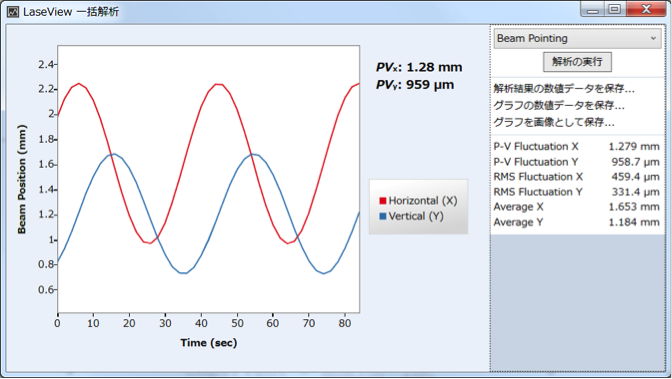
Fig: Beam pointing stability screen
- Use the image logging function, and save images taken at an appropriate time interval.
- Click the “Pointing” button.
- Click the “Execute analysis”.
The changes over time of X and Y coordinates of the beam centroid will be displayed in a graph.
Multi-point analysis function in LaseView
Case1:Analysis usage example with multiple “LBP-B”
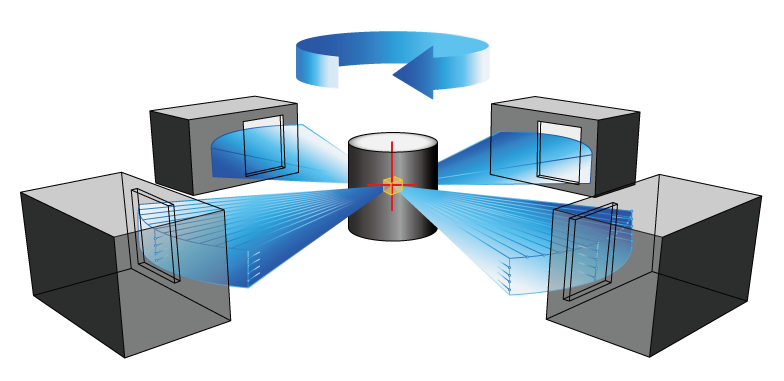
Fig: 90 degrees in the circumferential direction
Case2:Analysis usage example with multiple “LBP-B”
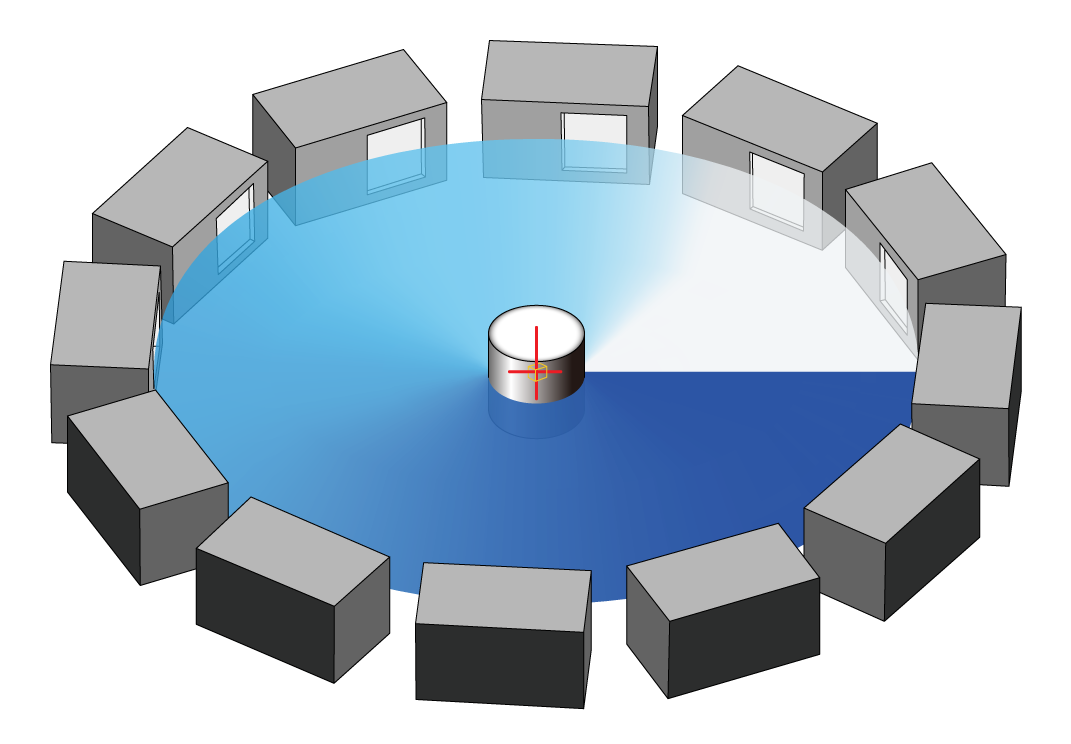
Fig: For the quarter in the circumferential direction, put 4 pieces together
Case3:Analysis usage example with multiple “LBP-B”
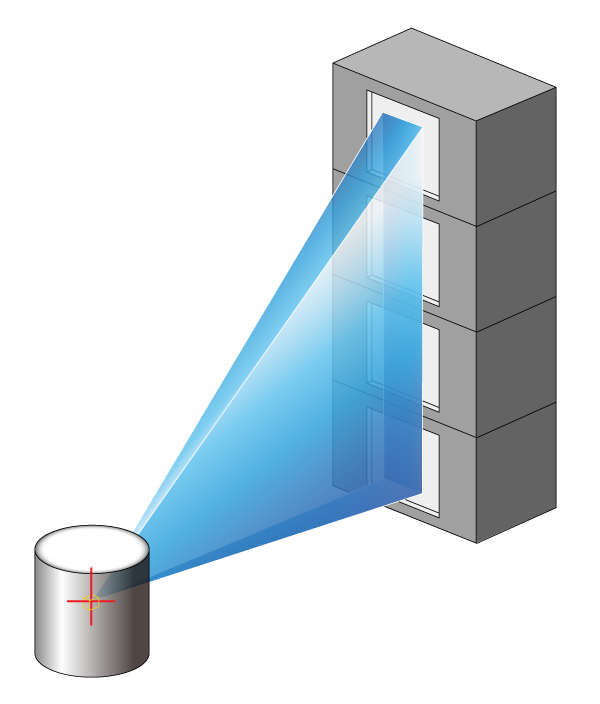
Fig: Stack four vertically
Case4:Analysis usage example with multiple “LBP-B”
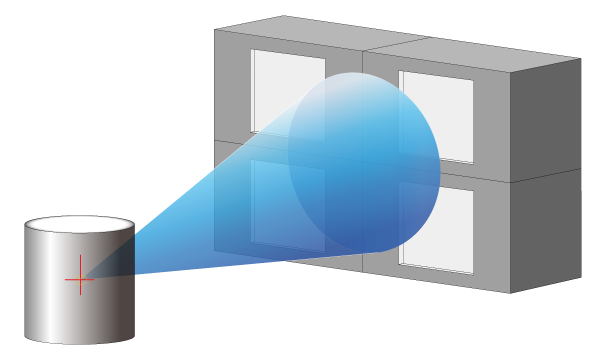
Fig: Arrange in 2 rows and 2 rows
Application
- Beam profile measurement for large diameter
- Beam profile measurement for high power laser
- Measurement for Laser far field pattern (FFP)
- Measurement for Laser near field pattern (NFP)
- Beam profile measurement for laser processing
- Beam profile measurement for surgical laser
- Measurement and evaluation of CW (continuous wavelength) and pulse LED emission
- Measurement and evaluation of beam of semiconductor laser emission
- Measurement and evaluation of beam of optical pick-up sources
- Measurement and evaluation of NA of optical fiber
- Measurement of propagation loss, beam profile or divergence angle for artificial star and distance measurement laser devices of astronomical telescopes
- Lensometer
- Beam monitoring system of long-distance propagating laser
- Beam profile measurement of laser scanning unit
- Scan laser position measurement
- For confirmation of Lidar laser
- Lidar rating
- RGB laser source position and beam profile measurement
- For confirmation of laser projector
Sales results
- Tokyo Institute of Technology
- Saga University
- Japan Coast Guard(JCG)
- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency(JAXA)
- National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology(QST)
- Japan Atomic Energy Agency(JAEA)
- More than 10 domestic private companies
- More than 2 overseas private companies